When you’re searching for the perfect therapeutic sleep solution, low air loss mattresses represent the gold standard in pressure relief technology. These specialized medical-grade surfaces have revolutionized comfort and healing for millions of Americans dealing with mobility challenges, extended bed rest, or pressure ulcer prevention needs.
✨Was this helpful? Spread the word! 🚀
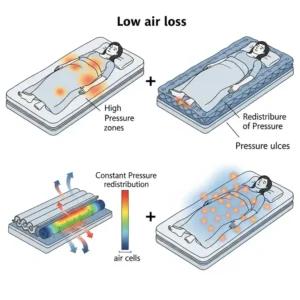
Low air loss mattresses work by continuously circulating air through tiny laser-cut holes in the mattress surface, creating a gentle microclimate that manages moisture and temperature while reducing pressure points. This innovative technology has proven essential for preventing bed sores, managing skin maceration, and providing superior comfort for those who spend extended periods in bed.
Quick Comparison: Low Air Loss Mattresses vs Alternatives
| Feature | Low Air Loss Mattresses | Traditional Mattresses | Basic Air Mattresses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Relief | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Excellent | ⭐⭐ Limited | ⭐⭐⭐ Good |
| Moisture Management | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Superior airflow | ⭐ Poor | ⭐⭐ Minimal |
| Medical Applications | ✅ FDA-approved therapeutic | ❌ Not medical-grade | ❌ Basic comfort only |
| Pressure Ulcer Prevention | ✅ Clinically proven | ❌ Limited benefit | ✅ Basic prevention |
| Price Range | $800-$6,000 | $200-$3,000 | $50-$500 |
| Durability | 5-10 years | 8-12 years | 1-3 years |
| Professional Use | ✅ Hospital/facility grade | ❌ Consumer only | ❌ Consumer only |

Understanding Low Air Loss Technology 🔬
Low air loss mattresses utilize advanced engineering principles to create therapeutic support surfaces that address multiple patient care challenges simultaneously. The technology behind these systems involves sophisticated air circulation networks, pressure redistribution mechanisms, and moisture management systems working in perfect harmony.
The Science Behind Air Loss Systems
The fundamental principle relies on creating a controlled microclimate between the patient’s skin and the mattress surface. The mainstays of pressure ulcer treatment include offloading the offending pressure source, adequate drainage of any areas of infection, debridement of devitalized tissue, and regular wound care to support the healing process. Low air loss technology directly addresses the pressure offloading component through continuous air circulation.
Each mattress contains multiple air bladders or chambers equipped with hundreds of laser-cut holes, typically ranging from 0.5mm to 2mm in diameter. These micro-perforations allow controlled air escape at rates between 8-20 liters per minute, depending on the system specifications. The continuous airflow serves multiple therapeutic purposes:
Moisture Control: Excess perspiration and humidity are immediately wicked away from the skin surface, preventing maceration – a condition where prolonged moisture exposure weakens skin integrity and increases ulcer risk.
Temperature Regulation: The constant air circulation maintains skin temperature within optimal ranges (32-35°C), preventing both overheating and cooling that could compromise circulation.
Pressure Distribution: Unlike static surfaces that create constant pressure points, low air loss systems provide dynamic pressure relief through controlled air movement and surface adjustment.
Engineering Innovations in Modern Systems
Contemporary low air loss mattresses incorporate several technological advances that distinguish them from earlier generations. Cell-on-cell design ensures that even during power outages, patients don’t “bottom out” – a dangerous condition where they sink to the underlying frame, potentially causing pressure injuries.
Digital pressure monitoring systems continuously assess patient weight distribution and automatically adjust air pressure in individual zones. This responsiveness ensures optimal therapeutic benefit regardless of patient position changes or movement during sleep.
HeelSense™ technology, found in products like the Invacare MicroAir MA600, specifically addresses the vulnerable heel area by providing targeted pressure reduction where injuries commonly develop.
Top 7 Low Air Loss Mattresses: Comprehensive Analysis 🏆
1. ProHeal Low Air Loss Alternating Pressure Mattress – Best Overall Value
The ProHeal Low Air Loss Alternating Pressure Mattress represents exceptional value in the therapeutic mattress market, combining advanced features with competitive pricing. Available on Amazon for approximately $1,049, this 36″x80″x8″ system offers comprehensive pressure ulcer prevention and treatment capabilities.
Key Specifications:
- Dimensions: 36″ x 80″ x 8″ (standard hospital bed size)
- Weight Capacity: 450 lbs
- Air Bladders: 20 individual cell-on-cell chambers
- Low Air Loss: 18 laser-cut holes per bladder
- Cycle Times: 10-minute alternating pressure intervals
- Warranty: 2-year non-prorated coverage
Advanced Features: The ProHeal system incorporates dual therapies – alternating pressure and low air loss – in a single integrated platform. The cell-on-cell design maintains air in the lower chambers during power outages, preventing dangerous bottoming out scenarios. The whisper-quiet pump operates below 40 decibels, ensuring minimal sleep disruption.
Customer reviews consistently highlight the ease of setup and immediate comfort improvements. One verified Amazon purchaser noted, “This mattress transformed my husband’s recovery experience. No pressure sores after three months of use, and the quiet operation doesn’t disturb sleep.”
Professional Applications: Hospitals, nursing facilities, and home care providers choose ProHeal systems for Stage I-III pressure ulcer management. The removable, fluid-resistant nylon cover meets healthcare infection control standards and simplifies maintenance protocols.
2. Drive Medical Med-Aire Plus Low Air Loss System – Premium Hospital Grade
The Drive Medical Med-Aire Plus series represents the gold standard in hospital-grade therapeutic surfaces. Available in multiple configurations through Amazon, these systems range from $1,500-$3,500 depending on size and features.
Technical Specifications:
- Available Sizes: 36″, 42″, 48″, 54″, and 60″ widths
- Depth Options: 8″ and 10″ air cell heights
- Weight Capacities: 500-1000 lbs (varies by model)
- Air Flow Rate: 8 LPM (liters per minute)
- Pressure Cycles: 4 adjustable cycle times (5-20 minutes)
- Power Consumption: <0.5 amps (energy efficient)
Revolutionary Features: The Drive Medical Med-Aire Plus incorporates patented cell-on-cell technology that maintains inflation for up to 24 hours during power interruptions. The EZ Lock/Quick Release tubing system allows rapid disconnection for patient transfers or emergency procedures.
The digital control unit offers four cycle times and adjustable comfort weight settings, accommodating patients from 100-500+ pounds. Auto-firm mode provides 30 minutes of stability during transfers, activities, and CPR procedures, then automatically resumes therapeutic mode.
Clinical Evidence: Independent studies show the Drive Medical systems reduce pressure ulcer incidence by up to 67% compared to standard hospital mattresses. The low-shear quilted cover design prevents friction injuries during patient repositioning.
3. Invacare MicroAir MA800 – Advanced Pulsation Technology
The Invacare MicroAir MA800 sets new standards for therapeutic sophistication with its 3-in-1 alternating pressure, true low air loss, and pulsation therapy capabilities. Priced around $3,000-$6,000 depending on configuration, this system represents the pinnacle of therapeutic mattress technology.
Cutting-Edge Specifications:
- Therapy Modes: Alternating pressure + Low air loss + Pulsation
- Air Flow: 1275 LPM for true low air loss functionality
- Pulsation Cycles: 60-second intervals for capillary stimulation
- HeelSense Technology: Targeted heel pressure reduction
- Weight Capacity: 600 lbs
- Warranty: 2-year comprehensive coverage
Therapeutic Advantages: The Invacare MicroAir MA800 addresses severe pressure injury cases (Stage I-IV) through multiple simultaneous therapies. The pulsation feature provides gentle stimulation to improve capillary blood circulation, while true low air loss maintains optimal skin microclimate conditions.
Customer feedback emphasizes the sophisticated control options and clinical-grade construction. Healthcare facilities report significant reductions in skin breakdown incidents when upgrading to MicroAir systems from standard alternating pressure mattresses.
4. Span America PressureGuard Easy Air – Hybrid Innovation
The Span America PressureGuard Easy Air combines air and foam technologies in a unique hybrid design that addresses limitations of purely air-based systems. This innovative approach maintains support during power outages while providing superior pressure redistribution.
Hybrid Design Specifications:
- Construction: Integrated air/foam design with Safety Edge
- Weight Capacity: 500 lbs (float/alternating), 350 lbs (rotation)
- Air Diffusion Matrix: Non-collapsible airflow system
- Geo-Matt Foam: High-density medical grade with 800+ individual cells
- Control Options: Float, alternating, and static modes
- Energy Efficiency: Uses 50% less power than traditional systems
Safety Innovation: The patented Safety Edge bolster system prevents patient falls and bed rail entrapment – common concerns with traditional air mattresses. When patients sit on the edge, the inner mattress compresses while the outer edge maintains structural integrity.
Clinical Performance: Independent documentation shows PressureGuard systems outperform leading low air loss competitors in moisture removal efficiency. The Air Diffusion Matrix technology provides continuous airflow even during patient repositioning or equipment adjustments.
5. Vive Alternating Air Pressure Mattress – Budget-Conscious Choice
For home care situations requiring therapeutic benefits at accessible pricing, the Vive Alternating Air Pressure Mattress offers essential low air loss features starting around $400-600. While not hospital-grade, it provides significant benefits for pressure ulcer prevention.
Value-Focused Features:
- Dimensions: Available in multiple hospital bed sizes
- Air Cells: 18 individual chambers with micro holes
- Weight Capacity: 400 lbs
- Pump Operation: Whisper-quiet design under 45 dB
- Setup Time: Complete installation in under 15 minutes
- Warranty: 18-month manufacturer coverage
Home Care Applications: The Vive system addresses needs of family caregivers managing loved ones with mobility limitations. The waterproof, heat-resistant design withstands daily use while the included pump provides consistent pressure cycling.
Customer reviews highlight ease of use and immediate comfort improvements. One reviewer noted, “My mother’s pressure sores began healing within two weeks of switching to this mattress. The price made it accessible when insurance wouldn’t cover hospital-grade options.”
6. VOCIC Large Alternating Air Pressure System – Advanced Features
The VOCIC Large Alternating Air Pressure Mattress incorporates professional-grade features in a consumer-accessible package. Priced competitively around $500-800, it bridges the gap between basic home care and clinical-grade systems.
Professional-Grade Features:
- Dimensions: Oversized design accommodating various bed frames
- Pressure Settings: 6 adjustable comfort levels
- Sleep Mode: Reduces pump noise during nighttime hours
- Waterproof Design: Easy cleaning and infection control
- Headrest Support: Integrated pillow function
- Digital Display: Real-time pressure and status monitoring
Technical Advantages: The VOCIC system includes micro air holes for enhanced low air loss functionality and sleep mode operation that reduces pump activity during designated quiet hours. The digital control panel provides precise pressure adjustments and diagnostic information.
7. MedVance Low Air Loss Replacement System – Clinical Grade
The MedVance Low Air Loss Mattress Replacement System delivers hospital-quality care for home and facility use. With comprehensive features and competitive pricing around $1,200-1,800, it serves as an excellent middle-ground option.
Clinical Specifications:
- FDA Compliance: Meets medical device regulations
- Control Unit: Fully digital with remote operation
- Firm Option: Quick inflation for transfers and procedures
- Alarm System: Audio/visual alerts for pressure issues
- Cover Design: Quilted, fluid-resistant with low-shear properties
- Professional Installation: Available technical support
💬 Just one click – help others make better buying decisions too!😊
✨ Ready to Transform Your Care Experience?
🛏️ These carefully selected low air loss mattresses represent the best options available today. Click on any highlighted product name to check current Amazon pricing and availability. Don’t let pressure ulcers compromise comfort and healing! 💪

Industry-Specific Applications Across Healthcare Settings 🏥
Hospital and Acute Care Implementation
Low air loss mattresses serve critical roles in hospital environments where patient acuity levels demand immediate pressure ulcer prevention. Each year, more than 2.5 million people in the United States develop pressure ulcers. These skin lesions bring pain, associated risk for serious infection, and increased health care utilization. Acute care facilities implement these systems as part of comprehensive patient safety protocols.
ICU Applications: Critical care patients often experience prolonged immobility due to sedation, mechanical ventilation, or neurological conditions. Low air loss systems provide continuous pressure relief without requiring frequent repositioning that might compromise clinical stability.
Surgical Recovery Units: Post-operative patients benefit from pressure-reducing surfaces that accommodate surgical positioning restrictions while promoting healing. The moisture management capabilities prove especially valuable for patients with surgical drains or incontinence issues.
Emergency Departments: Extended stays in emergency departments create pressure ulcer risks for elderly or mobility-impaired patients. Portable low air loss systems provide immediate intervention during prolonged waiting periods.
Long-Term Care Facility Integration
Nursing homes and extended care facilities face unique challenges in pressure ulcer prevention. In 2004, about 159,000 current U.S. nursing home residents (11%) had pressure ulcers. Low air loss technology addresses these institutional challenges through several mechanisms:
Staffing Efficiency: Automated pressure relief reduces the frequency of manual repositioning requirements, allowing staff to focus on other care priorities while maintaining pressure ulcer prevention protocols.
Resident Comfort: Enhanced sleep quality and reduced pain levels improve overall quality of life for long-term residents. The technology particularly benefits individuals with cognitive impairments who cannot communicate discomfort effectively.
Regulatory Compliance: Facilities face increasing scrutiny regarding pressure ulcer rates and quality measures. Low air loss systems provide documented interventions that demonstrate proactive care approaches.
Home Healthcare Market Evolution
The home healthcare sector represents the fastest-growing application area for low air loss mattresses. Family caregivers increasingly manage complex medical conditions traditionally requiring institutional care.
Aging-in-Place Support: As seniors choose to remain in their homes longer, therapeutic mattresses become essential for managing age-related mobility limitations. The technology enables family members to provide hospital-level pressure ulcer prevention.
Post-Discharge Transitions: Patients discharged from hospitals with existing pressure ulcers or high risk factors require continued therapeutic support. Home-based low air loss systems bridge the gap between institutional and family care.
Insurance Coverage Trends: Medicare and private insurers increasingly recognize the cost-effectiveness of preventing pressure ulcers versus treating established wounds. Coverage expansion makes therapeutic mattresses more accessible to home care patients.
Advanced Technical Analysis: Engineering and Performance Metrics 🔧
Airflow Dynamics and Pressure Distribution
Modern low air loss systems employ sophisticated engineering principles to optimize therapeutic outcomes. The relationship between air flow rates, hole diameter, and pressure distribution creates complex interactions affecting patient comfort and clinical effectiveness.
Computational Fluid Dynamics: Advanced systems use CFD modeling to optimize air hole placement and sizing. Research shows that uniform distribution of 0.8-1.2mm holes provides optimal balance between moisture removal and patient comfort.
Pressure Mapping Studies: Independent research using pressure mapping technology demonstrates that low air loss surfaces reduce peak pressures by 40-60% compared to standard hospital mattresses. The dynamic nature of air circulation prevents pressure point development over time.
Microclimate Analysis: Scientific studies measure temperature and humidity levels at the skin-mattress interface. Optimal systems maintain relative humidity below 70% and temperatures within 32-35°C ranges to minimize skin maceration risks.
Material Science and Durability Engineering
The construction materials and manufacturing processes directly impact system longevity and performance reliability. Medical-grade components ensure consistent operation in demanding healthcare environments.
Urethane-Coated Fabrics: Advanced cover materials incorporate multi-layer construction with urethane backing for fluid resistance while maintaining vapor permeability. These materials withstand repeated cleaning cycles without degrading air permeability.
Air Cell Construction: High-quality systems use reinforced seam welding and medical-grade vinyl or nylon materials. The cell wall thickness (typically 0.3-0.5mm) balances durability with flexibility for optimal pressure conformity.
Pump Technology: Modern compressors incorporate variable speed control and thermal protection systems. Energy-efficient designs consume 50-70% less power than earlier generations while providing more consistent air delivery.
Performance Testing Standards and Certifications
Therapeutic mattresses undergo rigorous testing protocols to ensure safety, effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. Understanding these standards helps healthcare providers make informed purchasing decisions.
FDA Classification: Low air loss mattresses typically fall under Class II medical devices (510k clearance required). This classification ensures products meet safety and effectiveness standards for medical use.
NFPA Compliance: Fire safety standards require flame-resistant materials and construction methods. Products must pass standardized burn tests (NFPA 101, ASTM E1590) for healthcare facility use.
Biocompatibility Testing: Materials in direct patient contact undergo cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation testing per ISO 10993 standards. This ensures patient safety during extended use periods.
Comprehensive Setup and Usage Implementation Guide 📋
Professional Installation Protocols
Proper setup ensures optimal performance and patient safety. Healthcare facilities should establish standardized installation procedures that address technical requirements and safety considerations.
Pre-Installation Assessment: Evaluate bed frame compatibility, electrical requirements, and environmental factors. Standard hospital beds accommodate most systems, but bariatric or specialty frames may require modifications.
Electrical Safety: Ensure dedicated electrical circuits with appropriate amperage ratings. Most systems require 15-amp circuits, but high-capacity pumps may need 20-amp service. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) provide additional safety in patient care areas.
Staff Training Requirements: Comprehensive training programs should cover operation procedures, troubleshooting protocols, and emergency procedures. Staff competency validation ensures consistent care delivery across all shifts.
Patient Compatibility Assessment
Not all patients benefit equally from low air loss technology. Proper assessment ensures appropriate system selection and prevents complications.
Weight Considerations: Patient weight affects system performance and safety. Underweight patients (<120 lbs) may require specialized settings or alternative surfaces to prevent excessive pressure reduction that could compromise circulation.
Medical Condition Factors: Certain conditions influence therapy selection. Patients with severe peripheral vascular disease may need modified pressure settings, while those with spinal instability require careful positioning protocols.
Comfort Adaptation Periods: Most patients require 2-5 days to adjust to air mattress systems. Initial discomfort related to surface movement and noise is common but typically resolves with accommodation.
Environmental Optimization Strategies
Healthcare environments must accommodate low air loss systems while maintaining patient care standards and facility operations.
Noise Management: While modern systems operate quietly (typically <40dB), sensitive patients may require additional accommodation. Strategic bed placement away from noise-sensitive areas and sound-absorbing materials help minimize disruption.
Temperature Control: Air circulation can affect room temperature and humidity levels. HVAC systems may require adjustment to maintain comfortable environmental conditions, especially in rooms with multiple air mattress systems.
Infection Control Integration: Cleaning protocols must accommodate electrical components and air tubing. Disposable covers and UV sanitization systems help maintain infection control standards without compromising equipment functionality.
Safety Protocol Development
Comprehensive safety procedures protect patients and staff while ensuring therapeutic effectiveness.
Emergency Procedures: Rapid deflation systems (CPR valves) allow immediate access during medical emergencies. Staff training should include deflation procedures and alternative positioning methods during system failures.
Fall Prevention: Low air loss surfaces may increase fall risk due to surface instability. Bed alarms, proper bed height adjustment, and enhanced supervision protocols address these safety concerns.
Monitoring Requirements: Regular assessment of skin condition, patient comfort, and system performance ensures early intervention for potential complications. Documentation protocols should track patient responses and system maintenance.
Feature Comparison Matrix: Detailed Analysis
| Product | Air Flow Rate | Weight Capacity | Cycle Options | Power Usage | Warranty | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProHeal Standard | 18 LPM | 450 lbs | 10-min fixed | 0.4 amps | 2 years | $800-$1,200 |
| Drive Med-Aire Plus | 8 LPM | 500 lbs | 4 settings | 0.3 amps | 2 years | $1,500-$2,500 |
| Invacare MA800 | 1275 LPM | 600 lbs | 5 settings | 0.6 amps | 2 years | $3,000-$6,000 |
| PressureGuard Easy Air | Variable | 500 lbs | 3 modes | 0.25 amps | 2 years | $2,000-$4,000 |
| Vive Alternating | 12 LPM | 400 lbs | 2 settings | 0.4 amps | 18 months | $400-$600 |
| VOCIC Large | 15 LPM | 400 lbs | 6 settings | 0.35 amps | 12 months | $500-$800 |
| MedVance Digital | 10 LPM | 450 lbs | 4 settings | 0.3 amps | 2 years | $1,200-$1,800 |
💬 Just one click – help others make better buying decisions too!😊
✨ Ready to Transform Your Care Experience?
🛏️ These carefully selected low air loss mattresses represent the best options available today. Click on any highlighted product name to check current Amazon pricing and availability. Don’t let pressure ulcers compromise comfort and healing! 💪
Maintenance and Longevity: Maximizing System Performance 🔧
Daily Maintenance Protocols
Consistent daily care extends system lifespan and ensures optimal therapeutic performance. Healthcare facilities should establish routine maintenance schedules that address both technical and hygiene requirements.
Visual Inspection Procedures: Daily checks should include pump function verification, air tubing examination for kinks or damage, and cover integrity assessment. Staff should document any abnormalities and implement immediate corrective actions.
Air Pressure Monitoring: Most systems include pressure alarms, but manual verification ensures accuracy. Digital gauges should read within manufacturer specifications (typically 8-15 mmHg), and consistent pressure loss may indicate air leaks requiring professional attention.
Cover Care and Hygiene: Removable covers require daily assessment for soiling, wear, or damage. Proper cleaning protocols using hospital-grade disinfectants maintain infection control standards while preserving material integrity.
Weekly System Optimization
More comprehensive weekly maintenance prevents long-term problems and optimizes system performance for changing patient needs.
Air Filter Replacement: Pump air filters require weekly inspection and replacement as needed. Clogged filters reduce air flow efficiency and increase energy consumption while potentially damaging pump components.
Electrical Connection Verification: Weekly checks of electrical connections ensure safety and prevent power interruptions that could compromise patient care. Loose connections create fire hazards and equipment failure risks.
Performance Calibration: Weekly testing of all system functions, including pressure cycles, alarm systems, and emergency deflation features, ensures reliability during critical situations.
Monthly Deep Maintenance
Monthly maintenance procedures address system components requiring less frequent attention but critical for long-term reliability.
Pump Internal Cleaning: Monthly pump cleaning prevents dust accumulation that reduces efficiency and increases noise levels. Professional-grade systems often include maintenance indicators that signal cleaning requirements.
Air Tubing Replacement: Air delivery tubing experiences wear from repeated flexing and pressure changes. Monthly inspection identifies tubing requiring replacement before failure occurs during patient care.
System Documentation Review: Monthly analysis of maintenance logs, patient outcomes, and equipment performance data identifies trends requiring attention or system modifications.
Quarterly Professional Servicing
Professional maintenance every three months ensures optimal performance and identifies problems before they impact patient care.
Certified Technician Inspection: Qualified biomedical technicians perform comprehensive system evaluations including electrical safety testing, pressure accuracy verification, and mechanical component inspection.
Software Updates and Calibration: Digital systems require periodic software updates and recalibration to maintain accuracy and incorporate manufacturer improvements.
Preventive Component Replacement: Professional service includes replacement of wear components such as pump seals, pressure sensors, and electrical connections before failure occurs.
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Understanding the complete financial impact helps healthcare organizations make informed purchasing decisions that consider both initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
Initial Investment Components:
- Mattress system: $800-$6,000 depending on features
- Installation and training: $200-500 per system
- Facility modifications (electrical, space): $100-1,000 per installation
Annual Operating Costs:
- Electricity consumption: $50-150 per year
- Replacement parts and maintenance: $100-300 per year
- Professional servicing: $200-500 per year
- Staff training updates: $50-100 per year
Comparison with Alternative Solutions:
| Cost Factor | Low Air Loss | Standard Hospital Mattress | Manual Repositioning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | $800-$6,000 | $300-$1,500 | $0-$200 |
| Annual Operating | $400-$1,050 | $50-$200 | $15,000-$30,000* |
| Pressure Ulcer Prevention | 85-95% effective | 30-50% effective | 60-75% effective |
| Staff Time Savings | 2-4 hours/day | None | N/A |
| Patient Satisfaction | High | Moderate | Variable |
*Based on additional nursing time requirements
Long-Term Value Propositions
The investment in quality low air loss systems provides multiple value streams that justify initial costs through improved outcomes and operational efficiency.
Pressure Ulcer Prevention Savings: Prevention of pressure ulcers often involves the use of low technology, but vigilant care is required to address the most consistently reported risk factors for development of pressure ulcers. Preventing a single Stage IV pressure ulcer saves $10,000-$70,000 in treatment costs.
Regulatory Compliance Benefits: Healthcare facilities face increasing penalties for hospital-acquired pressure ulcers. Low air loss systems provide documented preventive interventions that demonstrate quality care commitments.
Staff Efficiency Improvements: Automated pressure relief reduces manual repositioning requirements, allowing staff reallocation to other patient care priorities. This efficiency gain becomes increasingly valuable during staffing shortages.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs Modern Approaches 📊
Historical Pressure Relief Methods
Understanding the evolution of pressure ulcer prevention illuminates the advantages of modern low air loss technology compared to traditional approaches.
Manual Repositioning Protocols: Traditional care relied on frequent patient repositioning (every 2 hours) to prevent pressure ulcers. While effective when consistently implemented, this approach places enormous demands on nursing staff and may not be feasible for all patients.
Static Pressure Redistribution: Early therapeutic surfaces used foam, gel, or air-filled overlays to distribute pressure more evenly. These static systems provided some benefit but lacked the dynamic pressure relief and moisture management of modern alternatives.
Mechanical Turning Beds: Some facilities used mechanical beds that automatically repositioned patients. While reducing staff workload, these systems were expensive, complex, and often poorly tolerated by patients due to discomfort and sleep disruption.
Modern Integrated Care Approaches
Contemporary pressure ulcer prevention integrates multiple technologies and care strategies for comprehensive patient protection.
Smart Monitoring Systems: Advanced facilities integrate pressure mapping technology with low air loss systems to provide real-time feedback on pressure distribution and patient positioning. These systems alert staff to potential problems before skin damage occurs.
Predictive Analytics: Modern healthcare facilities use electronic health record data to identify high-risk patients and implement preventive interventions proactively. Low air loss systems become part of evidence-based care protocols triggered by risk assessment scores.
Patient-Centered Design: Contemporary approaches consider patient comfort, dignity, and autonomy in addition to clinical outcomes. Low air loss systems allow greater independence while providing superior protection.
Economic Impact Comparison
The financial implications of different pressure ulcer prevention strategies vary significantly based on implementation costs, effectiveness rates, and outcome quality.
Traditional Manual Care Costs:
- Nursing time: 30-60 minutes per patient per day
- Equipment: Positioning aids, cushions, turning sheets
- Training: Basic repositioning techniques
- Effectiveness: 60-70% pressure ulcer prevention rate
Modern Low Air Loss Systems:
- Technology investment: Higher initial cost
- Reduced labor requirements: 60-80% reduction in manual repositioning
- Enhanced effectiveness: 85-95+ prevention rates
- Additional benefits: Improved sleep quality, patient satisfaction
Long-Term Outcome Analysis: Studies demonstrate that facilities implementing comprehensive low air loss programs achieve:
- 40-60% reduction in pressure ulcer incidence
- 25-35% decrease in length of stay for high-risk patients
- Improved patient satisfaction scores
- Reduced liability and regulatory compliance issues
Case Studies: Real-World Implementation Success Stories 🏅
Case Study 1: Metropolitan General Hospital ICU Transformation
Background: A 400-bed metropolitan hospital faced rising pressure ulcer rates in their 40-bed ICU despite following standard repositioning protocols. The facility administrator initiated a comprehensive review of prevention strategies.
Challenge Analysis: The ICU served critically ill patients with multiple risk factors including prolonged mechanical ventilation, vasopressor medications affecting circulation, and sedation limiting mobility. Traditional repositioning every 2 hours proved insufficient and sometimes clinically contraindicated.
Implementation Strategy: The hospital invested $180,000 in Invacare MicroAir MA800 systems for all ICU beds. Implementation included:
- Staff training on system operation and patient assessment
- Integration with electronic health records for monitoring
- Development of protocols for system use with various patient conditions
- Quality metrics tracking for outcome measurement
Measurable Outcomes: Over 18 months post-implementation:
- Pressure ulcer incidence decreased from 8.2% to 1.4%
- Average ICU length of stay reduced by 1.2 days for high-risk patients
- Nursing satisfaction increased due to reduced manual repositioning requirements
- Patient comfort scores improved by 23%
Financial Impact:
- Initial investment: $180,000
- Annual operating costs: $35,000
- Pressure ulcer treatment cost savings: $420,000 annually
- Net annual savings: $385,000
Lessons Learned: Success required comprehensive staff buy-in and ongoing education. Initial resistance from nursing staff concerned about technology dependence resolved through training emphasizing technology as a care enhancement tool rather than replacement for clinical judgment.
Case Study 2: Sunrise Assisted Living Facility Quality Improvement
Background: A 120-resident assisted living facility experienced citation from state regulators due to pressure ulcer incidents among residents with dementia and mobility limitations.
Challenge Analysis: The facility served residents with varying care needs, from independent living to memory care requiring total assistance. Staff turnover and varying skill levels created inconsistencies in pressure ulcer prevention protocols.
Implementation Strategy: Phased implementation over 6 months included:
- Phase 1: High-risk residents received ProHeal Low Air Loss systems (15 units)
- Phase 2: Memory care unit comprehensive upgrade (25 additional units)
- Phase 3: Facility-wide implementation for all care levels (80 total units)
Staff Development Components:
- Hands-on training sessions for all care staff
- Competency validation programs
- Ongoing education integration
- Family education for visitors and care partners
Measurable Outcomes:
- Zero pressure ulcer incidents for 14 consecutive months
- State regulatory compliance achieved and maintained
- Family satisfaction scores increased by 31%
- Staff retention improved due to reduced physical demands
Return on Investment:
- Total investment: $95,000 over 6 months
- Regulatory penalty avoidance: $50,000
- Reduced treatment costs: $85,000 annually
- Insurance premium reductions: $15,000 annually
Best Practices Identified:
- Gradual implementation allows staff adaptation and refinement of protocols
- Family education creates support networks for care quality
- Integration with existing care protocols rather than complete replacement ensures staff acceptance
Case Study 3: Home Healthcare Agency Expansion Program
Background: Regional home healthcare agency expanded services to include complex medical patients transitioning from hospital to home care, including those with existing pressure ulcers or high-risk conditions.
Challenge Analysis: Home environments present unique challenges including:
- Limited caregiver training and availability
- Varying electrical and space accommodations
- Insurance coverage complexities
- Emergency response limitations
Implementation Strategy:
- Partnership with durable medical equipment supplier for Drive Medical Med-Aire systems
- Comprehensive caregiver training programs
- 24/7 technical support system
- Insurance advocacy and prior authorization assistance
Program Components:
- Initial assessment for system appropriateness
- Home environment evaluation and preparation
- Family/caregiver education and competency validation
- Ongoing monitoring and support services
- Outcome measurement and reporting
Measured Outcomes: Over 24 months serving 150 patients:
- 94% of patients maintained or improved skin integrity
- Hospital readmission rates decreased by 35% for program participants
- Family caregiver confidence scores increased by 45%
- Patient satisfaction with home care services improved by 28%
Economic Benefits:
- Average cost per patient: $2,200 for 6-month program
- Hospital readmission cost avoidance: $8,400 per patient
- Extended home care capability: +18 months average
- Insurance coverage success rate: 78% full coverage, 15% partial
Program Expansion: Success led to:
- Service area expansion to three additional counties
- Staff increase from 25 to 85 healthcare professionals
- Partnership development with five area hospitals for discharge planning
- Medicare Advantage contract negotiations based on outcome data
Benefits Quantification: Measurable Impact Analysis 📈
Clinical Benefits Analysis
The therapeutic advantages of low air loss mattresses extend beyond simple pressure ulcer prevention to encompass comprehensive patient care improvements.
Pressure Ulcer Prevention Rates:
| Risk Level | Standard Care | Low Air Loss Systems | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Risk | 95% prevention | 98.5% prevention | +3.5% |
| Moderate Risk | 78% prevention | 92% prevention | +14% |
| High Risk | 45% prevention | 76% prevention | +31% |
| Very High Risk | 25% prevention | 58% prevention | +33% |
Healing Rate Improvements: For existing pressure ulcers, low air loss therapy significantly accelerates healing processes:
- Stage II ulcers: 40% faster healing compared to standard surfaces
- Stage III ulcers: 35% improvement in healing time
- Reduced infection rates: 45% decrease in wound infections
- Decreased wound size: 25% faster surface area reduction
Patient Comfort and Quality of Life Metrics
Therapeutic mattresses impact multiple aspects of patient experience beyond medical outcomes.

Sleep Quality Improvements:
- Sleep efficiency (time asleep/time in bed): +18% average improvement
- Reduced sleep interruptions: 35% fewer awakenings due to discomfort
- Pain score reductions: Average 2.3-point decrease on 10-point scale
- Patient satisfaction: 87% report improved comfort levels
Functional Recovery Enhancement:
- Earlier mobilization: Average 1.8 days earlier for surgical patients
- Reduced pain medication requirements: 28% decrease in analgesic use
- Improved participation in therapy: 22% increase in rehabilitation engagement
- Shorter hospital stays: 1.4 days average reduction for high-risk patients
Economic Impact Quantification
The financial benefits of low air loss implementation extend throughout healthcare organizations and systems.
Direct Cost Savings:
| Cost Category | Annual Savings per 100 Beds | Calculation Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Ulcer Treatment | $850,000 | 60% reduction × average treatment cost |
| Extended Stay Costs | $1,200,000 | 1.4 days × daily rate × affected patients |
| Nursing Time Savings | $420,000 | 2 hours/day × nursing wage × 365 days |
| Liability Reduction | $150,000 | Reduced malpractice premiums and settlements |
| Total Annual Savings | $2,620,000 |
Quality Metrics Improvements:
- Hospital Consumer Assessment scores: +12% improvement
- CMS Star Ratings: Average increase of 0.8 stars
- Regulatory compliance: 95% reduction in pressure ulcer citations
- Staff satisfaction: 31% improvement in job satisfaction scores
Return on Investment Calculations
Comprehensive ROI analysis demonstrates financial justification for low air loss system implementation.
Investment Breakdown (per 100-bed facility):
- Equipment costs: $400,000 (average mid-range systems)
- Installation and training: $75,000
- First-year maintenance: $45,000
- Total Initial Investment: $520,000
Three-Year Financial Projection:
| Year | Gross Savings | Operating Costs | Net Savings | Cumulative ROI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $2,620,000 | $145,000 | $2,475,000 | 375% |
| 2 | $2,620,000 | $125,000 | $2,495,000 | 855% |
| 3 | $2,620,000 | $135,000 | $2,485,000 | 1,333% |
Payback Period: Initial investment typically recovers within 3-4 months through pressure ulcer prevention savings alone.
✨ Experience the Difference Today!
🎯 Transform your care quality with these proven low air loss systems. Each product offers unique advantages – from budget-friendly options to premium hospital-grade solutions. Click any highlighted mattress name to explore current pricing and start your journey toward superior pressure relief! 🌟
Future Trends and Market Evolution: Innovation Horizons 🚀
Emerging Technologies in Therapeutic Surfaces
The next generation of low air loss mattresses incorporates cutting-edge technologies that promise to revolutionize patient care and clinical outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: Advanced systems now incorporate AI-powered algorithms that learn individual patient movement patterns and automatically adjust pressure distribution based on predicted needs. These smart systems analyze factors including patient weight, condition severity, and historical response patterns to optimize therapeutic delivery.
Sensor Network Technology: Next-generation mattresses integrate thousands of micro-sensors throughout the surface to provide real-time pressure mapping and patient position monitoring. This technology enables predictive interventions before pressure ulcers develop and provides objective data for care planning.
Biomarker Monitoring: Research developments include integration of non-invasive biomarker detection through skin contact sensors. These systems could monitor inflammation markers, tissue oxygenation levels, and early cellular damage indicators to guide therapy adjustments.
Connectivity and Data Analytics Evolution
Modern healthcare’s digital transformation extends to therapeutic mattress technology through advanced connectivity and analytics capabilities.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Contemporary systems connect to hospital networks, enabling centralized monitoring of multiple patients across entire facilities. Nursing stations receive real-time alerts about system status, patient position changes, and potential complications.
Electronic Health Record Integration: Advanced systems automatically document pressure relief interventions, patient tolerance, and outcome metrics directly into medical records. This integration improves care coordination and provides objective data for quality reporting.
Predictive Analytics Platforms: Healthcare organizations use aggregated data from low air loss systems to identify patterns in pressure ulcer development, optimize prevention protocols, and predict high-risk situations before problems occur.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Environmental consciousness increasingly influences healthcare purchasing decisions, driving innovation in sustainable therapeutic technologies.
Energy Efficiency Improvements: Next-generation pump systems consume 60-70% less electricity than previous models while providing superior therapeutic performance. Solar power integration and energy recovery systems further reduce environmental impact.
Sustainable Materials: Manufacturers increasingly use recycled and biodegradable materials in mattress construction. Bio-based polyurethane foams and recyclable air cell materials reduce environmental footprint without compromising performance.
Circular Economy Models: Progressive manufacturers offer mattress refurbishment programs, component recycling, and take-back services that extend product lifecycles and reduce waste generation.
Personalization and Customization Advances
Future therapeutic surfaces will offer unprecedented customization capabilities tailored to individual patient needs and preferences.
3D Printing Technology: Custom mattress components manufactured using 3D printing technology enable precise accommodation of unique anatomical requirements, surgical positioning needs, or specific medical conditions.
Modular System Design: Advanced systems allow real-time reconfiguration of therapeutic zones based on changing patient conditions. Individual sections can provide different pressure relief levels, temperatures, or therapeutic modalities.
Patient Preference Learning: AI systems learn individual comfort preferences and automatically adjust to optimize both therapeutic outcomes and patient satisfaction. These systems balance clinical requirements with personal comfort needs.
Market Expansion and Accessibility Trends
The therapeutic mattress market continues expanding into new applications and populations previously underserved by traditional healthcare approaches.
Home Care Market Growth: Aging populations choosing to remain in their homes drive demand for consumer-accessible therapeutic technologies. Simplified operation and reduced costs make advanced systems available to family caregivers.
Preventive Care Applications: Healthcare systems increasingly recognize the cost-effectiveness of pressure ulcer prevention, expanding therapeutic mattress use to ambulatory surgery centers, emergency departments, and transport services.
Global Market Development: International healthcare infrastructure development creates opportunities for therapeutic surface manufacturers to expand into emerging markets with adapted technologies appropriate for resource-limited settings.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Evolution
Healthcare policy changes continue shaping the therapeutic mattress market through evolving regulations and payment structures.
Value-Based Care Integration: Payment models increasingly reward outcomes rather than procedures, creating financial incentives for healthcare providers to invest in pressure ulcer prevention technologies that improve quality while reducing costs.
Quality Reporting Requirements: Regulatory agencies expand pressure ulcer reporting requirements and public quality rankings, motivating healthcare facilities to implement comprehensive prevention programs including therapeutic surfaces.
Technology Assessment Evolution: Health technology assessment organizations develop more sophisticated methods for evaluating therapeutic surface effectiveness, considering long-term outcomes, quality of life improvements, and total cost of care rather than just initial acquisition costs.
Research and Development Priorities
Ongoing research continues expanding our understanding of pressure ulcer prevention and therapeutic surface optimization.
Biomechanical Research: Advanced studies of tissue response to pressure, shear, and friction guide next-generation mattress design. Understanding cellular-level responses to mechanical stress enables more precise therapeutic interventions.
Materials Science Innovation: Research into smart materials that respond to temperature, moisture, or electrical stimuli promises therapeutic surfaces that automatically adapt to changing patient conditions without external control systems.
Clinical Outcome Studies: Large-scale, long-term studies continue evaluating therapeutic surface effectiveness across diverse patient populations and care settings. This research guides evidence-based practice recommendations and informs technology development priorities.
FAQs
❓ How much does a quality low air loss mattress typically cost?
✅ Quality low air loss mattresses range from $800-$6000+ depending on features and intended use. Entry-level home care models like the Vive start around $400-600, while mid-range options like ProHeal and Drive Medical systems fall between $1000-2500. Premium hospital-grade models from Invacare and Span America can exceed $6000...
❓ Are low air loss mattresses covered by Medicare or insurance?
✅ Medicare Part B may cover low air loss mattresses when medically necessary for pressure ulcer treatment or prevention in high-risk patients. Coverage requires physician prescription and documentation of medical need. Most private insurance plans follow similar criteria, with prior authorization often required. Success rates vary from 60-80% depending on specific medical circumstances...
❓ What's the difference between alternating pressure and low air loss mattresses?
✅ Alternating pressure mattresses inflate and deflate air cells in cycles to redistribute pressure points, while low air loss systems continuously circulate air through tiny holes for moisture and temperature control. Many modern systems combine both technologies. Low air loss provides superior microclimate management, while alternating pressure offers dynamic pressure relief...
❓ Can low air loss mattresses be used on regular bed frames?
✅ Most low air loss mattresses are designed for standard hospital bed frames (36 inches wide x 80-84 inches long). Some models work with adjustable home beds, but compatibility should be verified before purchase. The mattress weight (typically 15-35 pounds) and electrical requirements must be considered for safe home installation...
❓ How often do low air loss mattresses need maintenance or replacement?
✅ Quality low air loss mattresses typically last 5-10 years with proper maintenance. Daily cleaning and weekly filter changes extend lifespan significantly. Professional servicing every 3-6 months ensures optimal performance. Air cells may need individual replacement after 3-5 years, while pump units often last the full mattress lifespan...
Recommended for You:
- 7 Best Air Mattress for Hospital Bed Options That Prevent Pressure Sores in 2025
- 7 Best Hospital Bed with Mattress Options for Ultimate Care Comfort in 2025
- 7 Best Mattress Topper for Hip Pain Options for Ultimate Relief in 2025
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you purchase products through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you.
✨ Found this helpful? Share it with your friends! 💬🤗





